FIPS Module Specification
This is a draft document
Cryptographic Module Specification
A series of security libraries present an application program interface (API) to client and server applications utilizing NSS. The libraries are compiled and built for specific platforms (see Platform List) and tagged with a release identifier to be published on mozilla.org. The release compliant with FIPS 140-2 is NSS 3.11.5.
The cryptographic module is defined to be a subset of the functions within these libraries. The subset is below the top layer of functions normally called by application programs, but the subset may be called by application programs directly if they so choose. Functions that are being certified include Triple DES(KO 1,2,3 56/112/168), AES(128/192/256), SHS (SHA-1, SHA-256, SHA-384, SHA-512), HMAC, DSA (512-1024), and RSA (1024-8092).
Module Components
NSS is a software cryptographic implementation. No hardware or firmware components are included. All input to the module is via function arguments; all output is returned to the caller either as return codes or as updated memory objects pointed to by some of the arguments.
|
Cryptographic Module |
Library Name |
|---|---|
| PKCS #11 | libsoftokn3 |
| FREEBL | libfreebl3* (one is selected at run time) |
Note: Filename extensions depend upon the target operating environment. For some CPUs libfreebl3 is distributed in more than one variant. The optimal version is selected at run time.
The NSS module depends on the following libraries outside the cryptographic boundary.
|
NSS Dependencies |
Library Name |
|---|---|
| Netscape Portable Runtime (NSPR) | libnspr4 |
| NSPR string functions | libplc4 |
| NSPR hashtables and arena pools | libplds4 |
The NSS module is used by the following higher-level NSS libraries outside the cryptographic boundary.
|
Higher-level NSS API |
Library Name |
|---|---|
| CRMF | libcrmf |
| S/MIME | libsmime3 |
| Certificate Management |
libnss3 |
| SSL | libssl3 |
| JAR | libjar |
| PKCS #5 | libnss3 |
| PKCS #12 | libsmime3 |
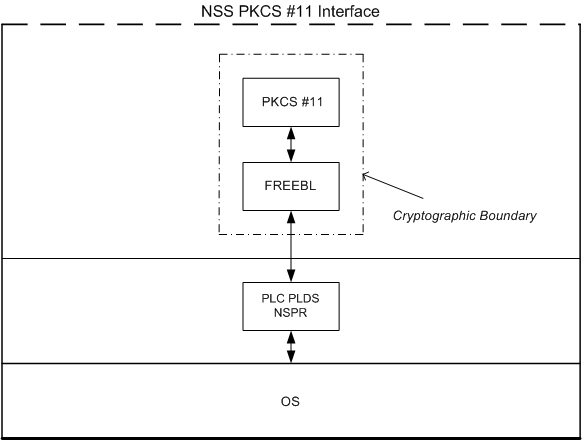
The Cryptographic Boundary
The NSS module is a multiple-chip standalone cryptographic module. The physical boundary of the NSS module is the enclosure of the general purpose computer it runs on, containing the processor(s) and other hardware components that store and protect the software components of the module.
NSS's PKCS #11 (Cryptoki) implementation forms the cryptographic module. The API itself is considered to define the logical cryptographic boundary, thus all implementation is considered below the boundary. Also included in this module is the FIPS PKCS #11 token. This is a Cryptoki token designed specifically for FIPS, and allows applications using NSS to operate in a strictly FIPS mode. The diagram below shows the relationship of the layers.
Approved Mode of Operation
In order to run the NSS module in the FIPS approved mode, an attribute must be explicitly set on the module. This can be done programmatically with a call to SECMOD_DeleteInternalModule() (with the module to delete being the internal module) or by running the NSS module utility modutil. An example command line is below.
modutil -fips true -dbdir certdir
The setting is permanent for the NSS module and all subsequent invocations of NSS functions using that cert directory will be in FIPS mode. The module can be taken out of FIPS mode by substituting false for true in the command above. The state of the module can be checked with:
modutil -chkfips true -dbdir certdir