FIPSFSM
This is a draft document.
We use an extended finite state model called Statecharts to specify the operation of the NSS cryptographic module. Statecharts, invented by David Harel to solve the state explosion problem of complex systems, extend the finite state model with two concepts:
- Hierarchical substates represent a refinement of a state, exposing more details. In addition to allowing us to specify a system's behavior at multiple levels of details, hierarchical substates can also reduce the number of transitions. A single transition leaving a composite state is equivalent to multiple transitions each leaving a hierarchical substate of the composite state. For example, transition 4.0 in our state transition diagram is such a transition.
- Concurrent substates represent concurrent subsystems that operate in parallel.
Statecharts have been adopted by the Unified Modeling Language (UML).
Finite State Model
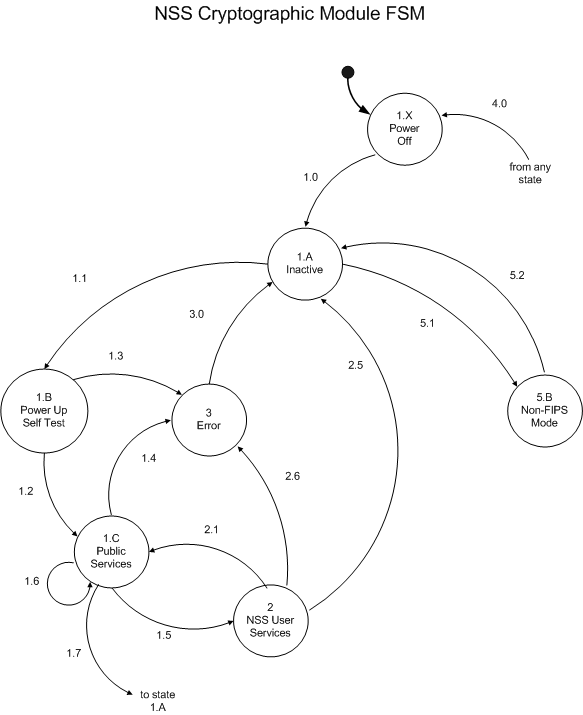
The state transition diagram of the NSS cryptographic module is shown below as a UML Statechart.
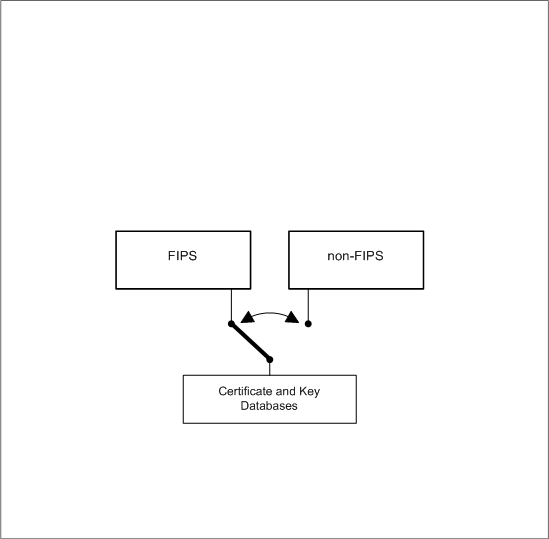
The NSS cryptographic module has two modes of operation: FIPS Approved mode and non-FIPS Approved mode. The two modes of operation are independent of each other -- they have their own copies of data structures and they are even allowed to be active at the same time. The two modes are represented by the two concurrent substates inside the Power On composite state. The module is FIPS 140-2 compliant only when the non-FIPS Approved mode is inactive (in state 5.A). The FIPS Approved mode on the left hand side is of more interest to the FIPS 140-2 validation and it is therefore shown with more details. When a program calls the FC_Initialize function of the NSS cryptographic module library, the state changes and power-up self-tests are performed. See Self Tests for a description of the power-up self-tests. If the self-tests succeed, the library is considered initialized for the FIPS Approved mode and the module enters the normal operational state. Please refer to the tables below when studying this state transition diagram.
Access to certificate and key databases: Only one of the two modes of operation may have the certificate and key databases open at any time. This is enforced by the FC_Initialize and NSC_Initialize functions. When a mode of operation opens the databases, it also causes the other mode (the peer) to close the databases. In the diagram below this is represented by a toggle switch.
Recovery from error states: If the FIPS Approved mode of the module ever enters the Error state, the NSS cryptographic module library needs to be shut down (transition 3.0) and reinitialized (transition 1.1).
Inclusive statement: The action of the finite state model as a result of all other combinations of data and control inputs is defined as follows.
- If the data and control inputs are valid and the module performs the service successfully, the module outputs the requested data or status information and returns
CKR_OK. - If the data and control inputs are invalid or the module encounters an error (e.g., running out of memory) when performing a service, the module does not output any data and simply returns an appropriate error code (e.g.,
CKR_HOST_MEMORY,CKR_TOKEN_WRITE_PROTECTED,CKR_TEMPLATE_INCOMPLETE, orCKR_ATTRIBUTE_VALUE_INVALID).
The module stays in the current state.
States
|
State Label |
State Mnemonic |
State Description |
Distinct Indicator |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.X | Power Off | Host computer is powered off. The initial state. | Host computer's power light is off. |
| 1.A | Inactive | Host computer is up and running. | Host computer's power light is on. |
| 1.B | Power Up Self Test | NSS cryptographic module library initialization for the FIPS Approved mode has been initiated. This state performs library initialization, software integrity test, and power-up self-tests. | The FC_Initialize call is executing.
|
| 1.C | Public Services | NSS cryptographic module library has been initialized for the FIPS Approved mode and its self-tests have passed. Services that do not require logging in to the module are available. | Public services can be invoked. Private services fail with the error code CKR_USER_NOT_LOGGED_IN.
|
| 2 | NSS User Services | Operator has successfully logged in to assume the NSS User role and has access to all the services provided by the FIPS Approved mode of the NSS cryptographic module. | All services can be invoked. |
| 3 | Error | The FIPS Approved mode of the NSS cryptographic module either has failed a conditional test while performing a service or has failed a power-up or operator-initiated self-test. No further cryptographic operations will be performed. | Only FC_Finalize, FC_InitToken, FC_CloseSession, FC_CloseAllSessions, FC_WaitForSlotEvent, and the "get info" functions (FC_GetFunctionList, FC_GetInfo, FC_GetSlotList, FC_GetSlotInfo, and FC_GetTokenInfo) can be invoked. FC_Initialize fails with the error code CKR_CRYPTOKI_ALREADY_INITIALIZED. All other functions fail with the error code CKR_DEVICE_ERROR.
|
| 5.B | Non-FIPS | The non-FIPS Approved mode of the NSS cryptographic module has been activated. This is a composite state whose substates are not relevant to FIPS 140-2. | NSC_Initialize has been called successfully. All other NSC_xxx functions may be called.
|
Transitions
|
Trans # |
Current State |
Next State |
Input Event |
Output Event |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | Power Off | Power On (states 1.A and 5.A) | Host computer is powered up | None |
| 1.1 | (FIPS Approved mode) Inactive | Power Up Self Test | FC_Initialize called |
Opens the databases. Causes the peer (non-FIPS Approved mode) to close the databases. Power-up self-tests initiated. |
| 1.2 | Power Up Self Test | Public Services | Successful library initialization, software integrity test, and power-up self-tests | FC_Initialize sets the internal Boolean state variable sftk_fatalError to false and returns CKR_OK
|
| 1.3 | Power Up Self Test | Error | Software integrity test or power-up self-test failure | FC_Initialize sets the internal Boolean state variable sftk_fatalError to true and returns CKR_DEVICE_ERROR
|
| 1.4 | Public Services | Error | Conditional self-test (continuous random number generator test) failed while performing a service (random number generation) | The function (FC_SeedRandom or FC_GenerateRandom) sets the internal Boolean state variable sftk_fatalError to true and returns CKR_DEVICE_ERROR
|
| 1.5 | Public Services | NSS User Services | User login succeeded | FC_Login sets the internal Boolean state variable isLoggedIn to true and returns CKR_OK
|
| 1.6 | Public Services | Public Services | User login failed | FC_Login returns a nonzero error code (e.g., CKR_PIN_INCORRECT)
|
| 1.7 | Public Services | (FIPS Approved mode) Inactive | FC_Finalize called |
FC_Finalize returns CKR_OK
|
| 2.1 | NSS User Services | Public Services | User logout requested | FC_Logout sets the internal Boolean state variable isLoggedIn to false and returns CKR_OK
|
| 2.5 | NSS User Services | (FIPS Approved mode) Inactive | FC_Finalize called |
FC_Finalize returns CKR_OK
|
| 2.6 | NSS User Services | Error | Conditional self-test (continuous random number generator test or pair-wise consistency test) failed while performing a service (random number generation or key pair generation) | The function (FC_SeedRandom, FC_GenerateRandom, or FC_GenerateKeyPair) sets the internal Boolean state variable sftk_fatalError to true and returns CKR_DEVICE_ERROR or CKR_GENERAL_ERROR
|
| 3.0 | Error | (FIPS Approved mode) Inactive | FC_Finalize called |
FC_Finalize returns CKR_OK
|
| 4.0 | Power On | Power Off | Host computer is powered off | None |
| 5.1 | (non-FIPS Approved mode) Inactive | (non-FIPS Approved mode) Activated | NSC_Initialize called |
Opens the databases. Causes the peer (FIPS Approved mode) to close the databases. NSC_Initialize returns CKR_OK.
|
| 5.2 | (non-FIPS Approved mode) Activated | (non-FIPS Approved mode) Inactive | NSC_Finalize called |
NSC_Finalize returns CKR_OK
|